ICM-42607-P | 6-axis MEMS IMU sensor

- Part No.:
- ICM-42607-P
- Manufacturer:
- TDK InvenSense
- Package:
- LGA-14(2.5x3)
- Description:
- MOTION SENSOR
- Quantity:
- Payment:

- Shipping:

Article Details
- Details
- Specifications
- Comparison
The ICM-42607-P is a high-performance 6-axis inertial measurement unit (IMU) sensor that integrates a 3-axis gyroscope and a 3-axis accelerometer. It is commonly used in scenarios requiring precise motion sensing and attitude tracking.
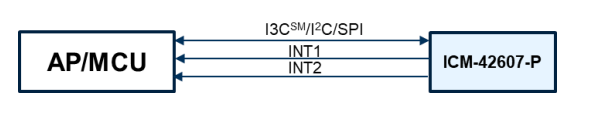
Get to Know ICM-42607-P
Highlights
- Configurable host interface supporting I3CSM, I2C and SPI serial communication
- Up to 2.25 KB FIFO and 2 programmable interrupts
- Supports ultra-low power motion wake-up to minimize system power consumption
- Supports the lowest gyroscope and accelerometer noise among such IMUs
- Features the highest stability against temperature, shock (up to 20,000g) or SMT/bending-induced offsets, as well as immunity to out-of-band vibration-induced noise
- Supports a VDD operating range of 1.71V to 3.6V
- Supports a separate VDDIO operating range of 1.71V to 3.6V
Features
- Gyroscope Noise: 7 mdps / Hz &Accelerometer Noise: 100 µg/Hz
- Low-Noise mode 6-axis current consumption of 0.55 mA
- Low-Power mode support for always-on experience
- User selectable Gyro Full-scale range (dps):± 250/500/1000/2000
- User selectable Accelerometer Full-scale range (g): ± 2/4/8/16
- User-programmable digital filters for gyro, accel , and temp sensor
- APEX Motion Functions: Pedometer, Tilt Detection, Low-g Detection, Freefall Detection, Wake on Motion, Significant Motion Detection
- Host interface: 12.5 MHz I3CSM, 1 MHz I2C,24 MHz SPI
Physical and Electrical Specifications
- Package Dimensions: 2.5 × 3 mm, 14-pin LGA small package, suitable for integration in space-constrained devices.
- Operating Voltage: 1.71 V ~ 3.6 V (VDD and VDDIO)
- Operating Temperature: −40 °C ~ +85 °C (typical industrial range).
- Output Resolution: 16-bit data output.
- Impact Resistance: Up to 20,000 g, enhancing mechanical reliability.
Applications
- Smartphones, Computers, Tablets
- Smart Watches and Fitness Trackers
- Augmented & Virtual Reality Headsets andControllers
- Game Controllers
- Drones and Robotics
Use ICM-42607-P
How does ICM-42607-P work?
1. The main modules and internal structure of the ICM-42607-P sensor:
- Three-axis MEMS gyroscope
- Three-axis MEMS accelerometer
- I3CSM, I2C, and SPI serial communications interfaces to Host
- Self-Test
- Sensor Data Registers
- FIFO
- Interrupts
- Digital-Output Temperature Sensor
- Bias and LDOs
- Charge Pump
- Standard Power Modes
- Utilizing the Coriolis effect
- Mechanical displacement of the vibrating structure is detected by capacitance
- The signal is amplified, demodulated, filtered, and ultimately converted into digital values
The ICM-42607-P includes a 3-axis MEMS accelerometer. Acceleration along a specific axis causes the displacement of the detection mass in the MEMS structure, and the capacitive sensor detects this displacement. The ICM-42607-P architecture reduces the sensitivity of the accelerometer to manufacturing variations and thermal drift. When the device is placed on a flat surface, the measured values on the X and Y axes are 0g, and the measured value on the Z axis is +1g. The ratio factor of the accelerometer is calibrated in the factory and is nominally independent of the power supply voltage. The full-scale range of the digital output can be adjusted to ±2g, ±4g, ±8g, and ±16g.
4. Signal processing mechanism
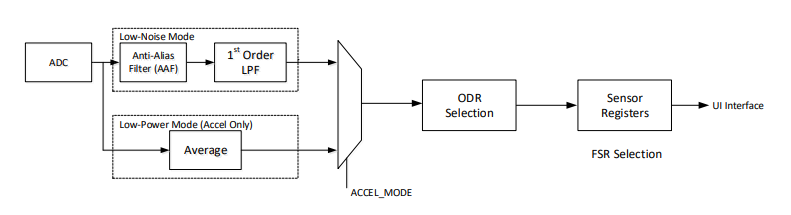
Key points of the ICM-42607-P signal path:
- The signal starts from the ADC of the gyroscope/accelerometer.
- Accelerometer: Supports low noise mode and low power consumption mode.
- Gyroscope: Only supports low noise mode.
- Low noise mode:
- ADC → Unconfigurable AAF → Configurable first-order LPF
- Low power consumption mode (only for the accelerometer):
- ADC → Configurable average filter
- After filtering, the ODR (Output Data Rate) is selected
- Finally, the FSR (Full Scale Range) is selected to determine the output range
QFA
Q1: What is the working principle of the accelerometer?The acceleration along a specific axis causes the MEMS to detect a change in mass position, and the capacitive sensor detects this displacement and converts it into a digital signal.
Q2: Which working modes are supported?
Accelerometer: Supports low-noise mode and low-power mode
Gyroscope: Only supports low-noise mode
Q3: Has the factory calibration been performed?
Yes, the scale factor of the accelerometer has been calibrated in the factory and is nominally independent of the power supply voltage.
- Product attributes
- Attribute value
- Manufacturer:
- TDK InvenSense
- Series:
- -
- Package/Case:
- LGA-14(2.5x3)
- Packaging:
- Tape & Reel (TR)
- Part Status:
- Active
- Resistance:
- Accelerometer, Gyroscope, 6 Axis
- Tolerance:
- -
- Composition:
- -
- Features:
- -
- Temperature Coefficient:
- -
- Operating Temperature:
- -
- Supplier Device Package:
- Power (Watts):
- -
- Ratings:
- Size / Dimension:
- Height - Seated (Max):
- Number of Terminations:
- Failure Rate:
| Image |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Part Number | ICM-42670-P | ICM-42605 | ICM-20602 | ICM-42688-P | ICM-20948 |
| Manufacturer | TDK InvenSense | TDK InvenSense | TDK InvenSense | TDK InvenSense | TDK InvenSense |
| Series | MotionTracking™ | - | - | - | - |
| Package/Case | 14-VFLGA | 14-VFLGA Module | 16-WFLGA Module | - | 24-TFQFN Module Exposed Pad |
| Packaging | Tape & Reel (TR) | Tape & Reel (TR) | Tape & Reel (TR) | Tape & Reel (TR) | Tape & Reel (TR) |
| Part Status | Active | Active | Not For New Designs | Active | Not For New Designs |
| Sensor Type | Accelerometer, Gyroscope, Temperature, 6 Axis | Accelerometer, Gyroscope, 6 Axis | Accelerometer, Gyroscope, Temperature, 6 Axis | Accelerometer, Gyroscope, 6 Axis | Accelerometer, Gyroscope, Magnetometer, 9 Axis |
| Output Type | I2C, SPI | I2C, I3C, SPI | I2C, SPI | - | I2C, SPI |
| Grade | - | - | - | - | - |
| Qualification | - | - | - | - | - |
| Supplier Device Package | 14-LGA (2.5x3) | 14-LGA (2.5x3) | 16-LGA (3x3) | - | 24-QFN (3x3) |
| Mounting Style | Surface Mount | Surface Mount | Surface Mount | - | Surface Mount |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C ~ 85°C | -40°C ~ 85°C | -40°C ~ 85°C | - | -40°C ~ 85°C |
inventory:10,000
Please send an inquiry. Send us your inquiry, and we will respond immediately.

-
BMI323
Bosch Sensortec

-
ICM-42670-P
TDK InvenSense

-
ICM-42605
TDK InvenSense

-
LSM6DSO32TR
STMicroelectronics

-
LSM6DSOTR
STMicroelectronics

-
LSM6DSVTR
STMicroelectronics