MT41K256M16 DDR3L SDRAM Working Principle | 4Gb 256Mx16 Memory

- Part No.:
- MT41K256M16TW-107 AAT:P
- Manufacturer:
- Micron Technology Inc.
- Package:
- 96-TFBGA
- Description:
- IC DRAM 4GBIT PAR 96FBGA
- Quantity:
- Payment:

- Shipping:

Article Details
- Details
- Specifications
- Comparison
In industrial and embedded applications, to achieve high-speed and reliable storage access while also providing low power consumption and multiple power-saving modes, the DDR3L SDRAM, a double data rate architecture, is often chosen to implement these high-speed operations. The MT41K256M16 is a typical representative of DDR3L SDRAM.
Notes: The double data rate architecture is an 8n-prefetch architecture, and its interface design enables the transmission of two data words on the I/O pins in each clock cycle.
How to correctly apply MT41K256M16?
The working principle of MT41K256M16
MT41K256M16, as DDR3L SDRAM, adopts a double data rate architecture to achieve high-speed operation. It has several key features:- There are 8 banks internally, which can be activated and operated simultaneously;
- CK/CK# differential clock is used, and DQS/DQS# signals are used for data alignment to improve signal integrity;
- Read and write accesses are in burst mode;
- It supports self-refresh mode and power-saving mode.
1. Selecting the row: When the controller issues the ACTIVATE command, the address bit corresponding to the ACTIVATE command is used to select the bank and row, preparing to access the data.
2. Selecting the column: By issuing the READ or WRITE command, the address bit corresponding to the READ/WRITE command is used to select the bank and the starting column for burst access. The DRAM accesses the data column by column.
3. Data transmission:
- DDR3L uses BL8 burst length: One command continuously transmits 8 data units.
- Internal 8n bit width, I/O port n bit width → Utilizing double data rate (DDR)
- Data is transmitted aligned along the DQS/DQS# signal.
- WRITE: The DQS signal is aligned with the data center.
- READ: The read data issued by DDR3 SDRAM is aligned with the edge of the DQS signal.
5. Parallel multi-bank operation: Supports concurrent operations, thereby improving bandwidth by hiding row pre-charging and activation times.
6. Low power mode:
- Self refresh: The chip automatically refreshes to maintain data.
- Power saving mode: Reduces current consumption.
How to use MT41K256M16 in applications
1. Embedded Applications
In industrial control boards or some industrial control computers, as well as edge computing devices, MT41K256M16 serves as the main running memory. The CPU accesses it through the DDR3 controller. The data bit width is 16 bits (1 chip → 16-bit DDR3 bus, 2 chips connected in parallel → 32-bit DDR3 bus).
2. Network Communication Devices
In industrial Ethernet switches or 5G edge gateways and routers applications, the network interface chips or the CPU first receive the data, then the data is written into MT41K256M16 SDRAM, and finally through burst continuous reading and writing to increase the throughput rate. It achieves high-speed burst access, which is very suitable for large data streams.
3. Display System
In industrial touch screens or medical display devices, MT41K256M16 serves as the image frame cache, storing display frames, graphic buffers, and UI rendering data.
4. Industrial Data Acquisition
In applications such as data acquisition cards, MT41K256M16 is used as a high-speed sampling data cache. From sampling to SDRAM and finally to the CPU/storage. It supports concurrent bank operations, reducing the risk of data loss.
5. Vehicle/Industrial-grade Systems
In vehicle infotainment systems, MT41K256M16 supports a wide temperature range and can operate 7*24 hours.
The differences between MT41K1G4, MT41K512M8, and MT41K256M16 in DDR3L SDRAM
|
model |
organization form |
capacity |
|
MT41K1G4 |
128M × 4 × 8 banks |
1 Gb |
|
MT41K512M8 |
64M × 8 × 8 banks |
512 Mb |
|
MT41K256M16 |
32M × 16 × 8 banks |
256 Mb |
Notes: They are all DDR3L SDRAM, featuring the same interface, timing specifications, voltage levels and functions. The only difference lies in the capacity and internal organization method (data width / bank count).
Common Questions about MT41K256M16
Q1: What are the differences between DDR3 and DDR3L?- DDR3: 1.5V
- DDR3L: 1.35V (compatible with some DDR3 controllers)
Q2: Is this a memory module? Can it be directly inserted into the motherboard?
No. MT41K256M16 is a bare-chip memory IC (FBGA package), which must be soldered onto the PCB and used through the DDR3 controller of the SoC. It cannot be plugged out or inserted like DIMM.
Q3: Can it be replaced with another brand?
Yes, but please confirm:
- DDR3L voltage compatibility
- Capacity and bit width consistency (256M × 16)
- FBGA packaging and pinout compatibility
- Product attributes
- Attribute value
- Manufacturer:
- Micron Technology Inc.
- Series:
- -
- Package/Case:
- 96-TFBGA
- Packaging:
- Tray
- Part Status:
- Active
- Resistance:
- Not Verified
- Tolerance:
- Volatile
- Composition:
- SDRAM - DDR3L
- Features:
- 4Gbit
- Temperature Coefficient:
- 256M x 16
- Operating Temperature:
- Parallel
- Supplier Device Package:
- 933 MHz
- Power (Watts):
- DRAM
- Ratings:
- -
- Size / Dimension:
- 20 ns
- Height - Seated (Max):
- 1.283V ~ 1.45V
- Number of Terminations:
- -40°C ~ 105°C (TC)
- Failure Rate:
- Automotive
| Image |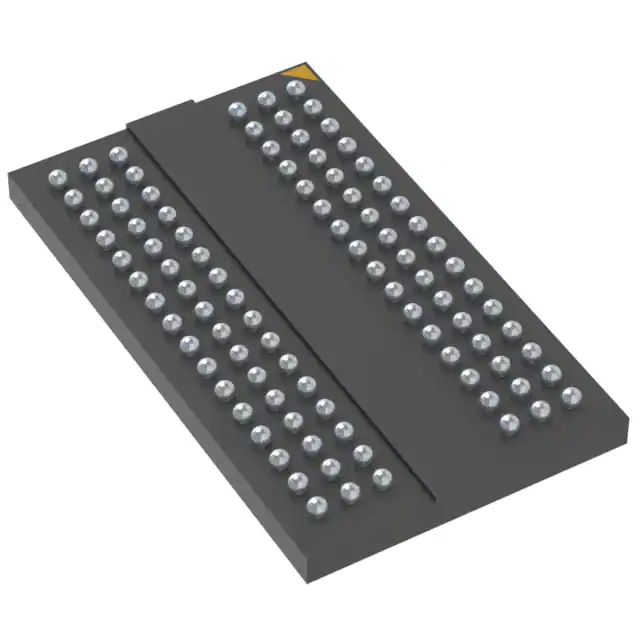  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Part Number | MT41K256M16TW-093:P | MT41K256M16TW-107 IT:P TR | MT41K256M16TW-107:P | MT41K256M16TW-107 IT:P | MT41K256M16TW-107 AIT:P TR |
| Manufacturer | Micron Technology Inc. | Micron Technology Inc. | Micron Technology Inc. | Micron Technology Inc. | Micron Technology Inc. |
| Series | - | - | - | - | - |
| Package/Case | 96-TFBGA | 96-TFBGA | 96-TFBGA | 96-TFBGA | 96-TFBGA |
| Packaging | Tray | Tape & Reel (TR) | Tray | Box | Tape & Reel (TR) |
| Part Status | Active | Active | Active | Active | Active |
| Programmable | Not Verified | Not Verified | Not Verified | Not Verified | Not Verified |
| Memory Type | Volatile | Volatile | Volatile | Volatile | Volatile |
| Technology | SDRAM - DDR3L | SDRAM - DDR3L | SDRAM - DDR3L | SDRAM - DDR3L | SDRAM - DDR3L |
| Memory Size | 4Gbit | 4Gbit | 4Gbit | 4Gbit | 4Gbit |
| Memory Organization | 256M x 16 | 256M x 16 | 256M x 16 | 256M x 16 | 256M x 16 |
| Supplier Device Package | 96-FBGA (8x14) | 96-FBGA (8x14) | 96-FBGA (8x14) | 96-FBGA (8x14) | 96-FBGA (8x14) |
| Memory Interface | Parallel | Parallel | Parallel | Parallel | Parallel |
| Clock Frequency | 1.066 GHz | 933 MHz | 933 MHz | 933 MHz | 933 MHz |
| Memory Format | DRAM | DRAM | DRAM | DRAM | DRAM |
| Write Cycle Time - Word, Page | - | 15ns | - | - | - |
| Access Time | 20 ns | 20 ns | 20 ns | 20 ns | 20 ns |
| Mounting Style | Surface Mount | Surface Mount | Surface Mount | Surface Mount | Surface Mount |
| Voltage - Supply | 1.283V ~ 1.45V | 1.283V ~ 1.45V | 1.283V ~ 1.45V | 1.283V ~ 1.45V | 1.283V ~ 1.45V |
| Qualification | - | - | - | - | AEC-Q100 |
| Operating Temperature | 0°C ~ 95°C (TC) | -40°C ~ 95°C (TC) | 0°C ~ 95°C (TC) | -40°C ~ 95°C (TC) | -40°C ~ 95°C (TC) |
| Grade | - | - | - | - | Automotive |
inventory:3,094
Please send an inquiry. Send us your inquiry, and we will respond immediately.
-
M24C02-WMN6TP
STMicroelectronics
-
AT24C02C-XHM-T
Microchip Technology

-
AT21CS01-STUM10-T
Microchip Technology
-
AT24C02C-SSHM-T
Microchip Technology
-
24LC01BT-I/OT
Microchip Technology
-
M24C02-FMC6TG
STMicroelectronics